Planning for a secure retirement is crucial, and building a solid retirement plan requires careful consideration of various factors. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps to ensure a comfortable and financially secure future, covering topics such as retirement savings, investment strategies, pension plans, Social Security benefits, and healthcare costs in retirement. Learn how to effectively manage your retirement portfolio, navigate tax implications, and create a personalized plan tailored to your specific needs and goals. Discover strategies for maximizing your retirement income and achieving financial freedom in your golden years.
Understanding Retirement Planning Basics
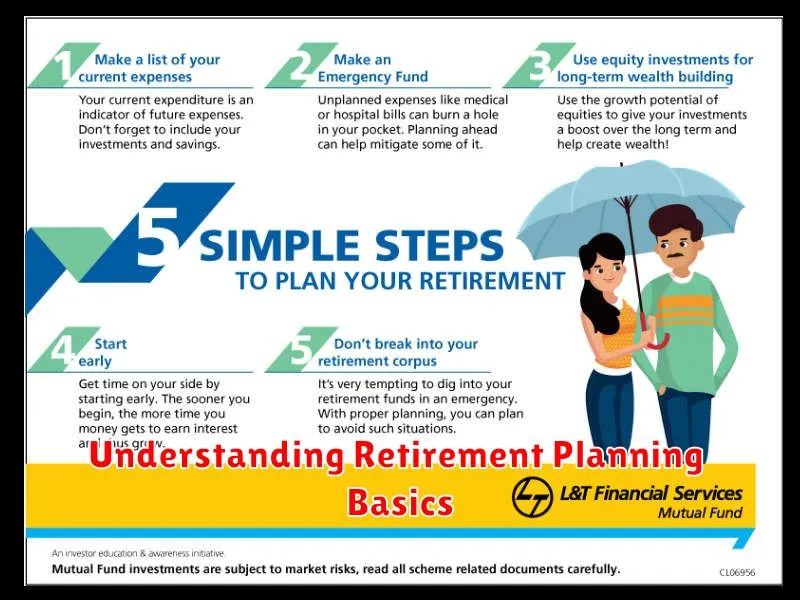
Retirement planning involves strategically saving and investing to ensure a comfortable financial future after you stop working. It’s a crucial process requiring careful consideration of various factors to ensure you have enough money to live on.
A fundamental aspect is determining your retirement goals. This includes estimating your desired lifestyle, considering inflation, and calculating how much you’ll need to maintain that lifestyle during retirement. Factors such as healthcare costs and potential long-term care needs should also be accounted for.
Understanding your current financial situation is equally critical. This involves assessing your assets (savings, investments, property), debts, and income. This assessment helps determine your starting point and identify areas requiring improvement. A realistic budget is essential for effective retirement planning.
Choosing the right investment strategies is key to growing your retirement savings. This might include a mix of stocks, bonds, and other investments, depending on your risk tolerance and time horizon. Diversification is important to mitigate risk.
Finally, regularly reviewing and adjusting your plan is vital. Your circumstances, goals, and the market fluctuate, so periodic adjustments will help you stay on track and adapt to changing conditions. Professional financial advice can be valuable in navigating this complex process.
How Much Should You Save for Retirement?
Determining how much you should save for retirement depends on several key factors. These include your desired lifestyle in retirement, your current age, your expected retirement age, and your current savings.
A common guideline suggests aiming to replace 80% of your pre-retirement income. However, this is a general rule of thumb and individual needs can vary significantly. Those with higher pre-retirement incomes or significant debts may require a higher savings target, while those with lower expenses might need less.
Financial professionals often utilize sophisticated calculations considering inflation, investment growth projections, and longevity to provide personalized estimates. Using online retirement calculators can also give you a preliminary idea, though professional advice is recommended for a comprehensive plan.
Ultimately, the amount you should save is a personal decision. Regularly reviewing your savings progress and adjusting your contributions as needed is crucial to ensure you’re on track to achieve your retirement goals.
Pension Plans vs 401(k) vs IRAs

Choosing the right retirement savings vehicle is crucial for a secure future. Three main options exist: pension plans, 401(k)s, and IRAs. Each has distinct features.
Pension plans, traditionally offered by employers, provide a guaranteed income stream upon retirement. Contributions are typically made by the employer, and the benefit amount is often calculated based on salary and years of service. However, pension plans are becoming increasingly rare.
401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement savings plans. Employees contribute pre-tax dollars, often matched by their employer up to a certain percentage. Investment choices are usually varied, offering flexibility but also requiring active management.
IRAs (Individual Retirement Accounts) are self-directed retirement savings plans. There are two main types: Traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs. Traditional IRAs offer tax-deductible contributions but taxable withdrawals in retirement, while Roth IRAs offer tax-free withdrawals in retirement but non-deductible contributions. Contribution limits apply to both.
The best option depends on individual circumstances, including employer benefits, income level, and risk tolerance. Diversification across multiple accounts is often recommended for a comprehensive retirement strategy.
Investment Strategies for a Secure Retirement
Building a secure retirement requires a well-defined investment strategy. Diversification is key; don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to mitigate risk.
Consider your risk tolerance. Younger investors can generally tolerate more risk, allowing for a higher allocation to stocks for potentially greater long-term growth. As retirement nears, a more conservative approach with a higher proportion of bonds becomes prudent to protect accumulated savings.
Dollar-cost averaging is a valuable strategy, involving regular investments regardless of market fluctuations. This helps mitigate the risk of investing a lump sum at a market peak. Rebalancing your portfolio periodically ensures your asset allocation remains aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Tax-advantaged accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, offer significant benefits by reducing your current tax burden and allowing your investments to grow tax-deferred or tax-free. Consult a financial advisor to determine the best approach for your specific circumstances and to develop a personalized retirement investment plan.
Regularly review and adjust your investment strategy as needed. Life circumstances change, and your investment plan should adapt accordingly to ensure you’re on track to achieve your retirement goals. Seeking professional advice from a qualified financial planner can provide valuable guidance and support throughout the process.
How to Minimize Taxes in Retirement

Minimizing your tax burden in retirement is crucial for preserving your hard-earned savings. Strategic planning is key to achieving this goal.
One important strategy is to understand the different types of retirement accounts and their tax implications. Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s offer tax deductions on contributions, but withdrawals are taxed in retirement. Conversely, Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s involve after-tax contributions, but withdrawals are tax-free in retirement. Choosing the right account aligns with your individual tax bracket and long-term financial goals.
Tax-efficient investing is another crucial aspect. Consider investments that generate lower taxable income, such as municipal bonds, which often offer tax-exempt interest. Consult a financial advisor to develop a diversified portfolio tailored to your retirement goals and risk tolerance.
Tax-loss harvesting can also be beneficial. This involves selling losing investments to offset capital gains taxes. It’s important to coordinate this strategy with your overall financial plan. Careful planning in this area can significantly reduce your tax liability.
Finally, stay informed about tax laws and regulations. Tax laws change, so staying updated ensures you’re using the most effective strategies. Consulting with a qualified tax professional is highly recommended to personalize your tax minimization plan.
The Role of Social Security Benefits
Social Security benefits play a crucial role in many retirees’ financial plans, providing a vital source of guaranteed income. Understanding how these benefits work is essential for building a solid retirement plan.
The amount of your monthly benefit depends on several factors, including your earnings history and your full retirement age (FRA). Claiming benefits earlier than your FRA results in a permanently reduced monthly payment, while delaying claiming can increase your monthly payment. Careful consideration of your individual circumstances is key to maximizing your Social Security benefits.
While Social Security is designed to supplement retirement income, it is rarely sufficient to cover all living expenses. Therefore, it’s vital to plan for additional income sources, such as personal savings, investments, or a pension. Viewing Social Security as a foundational component of your overall retirement strategy is crucial for a secure financial future.
Furthermore, it’s important to stay informed about potential changes to Social Security benefits and policies. Regularly reviewing your statement and understanding your eligibility options can help you make informed decisions to optimize your retirement income.
Estate Planning and Wealth Transfer

A solid retirement plan isn’t just about accumulating wealth; it’s also about preserving and distributing it effectively. Estate planning plays a crucial role in this process.
Estate planning encompasses the legal and financial strategies you implement to manage your assets during your lifetime and after your death. This includes creating a will or trust to determine how your assets will be passed on to your heirs. A well-structured plan minimizes estate taxes and ensures a smooth transfer of wealth to your beneficiaries.
Wealth transfer is the process of passing on your accumulated assets to your chosen beneficiaries. This can involve transferring assets directly during your lifetime (through gifts or trusts) or leaving them to your heirs upon your death. Careful planning helps you control how and when assets are transferred, minimizing potential legal disputes and maximizing tax efficiency.
Key elements of effective estate planning for retirement include: determining beneficiaries, creating a will or trust, understanding tax implications, naming a power of attorney, and establishing healthcare directives. Consulting with a financial advisor and estate planning attorney is highly recommended to create a personalized plan tailored to your specific circumstances.
Adjusting Your Retirement Plan Over Time
A well-structured retirement plan isn’t static; it requires regular review and adjustments to account for life’s changes. Regular adjustments are crucial for ensuring your plan stays on track to meet your goals.
Major life events such as marriage, divorce, the birth of a child, or a change in career significantly impact your financial situation and retirement needs. These events necessitate a reassessment of your savings goals, investment strategy, and withdrawal plan.
Economic shifts also demand attention. Market fluctuations, inflation, and changes in interest rates can influence the performance of your investments and necessitate adjustments to your asset allocation to mitigate risk and maintain your desired return.
Health changes can drastically alter your retirement expectations. Unexpected medical expenses can deplete savings, requiring adjustments to your spending plan or increased contributions to compensate for potential shortfalls.
Regularly review your retirement plan at least annually, or more frequently if significant life events occur. Consider consulting with a financial advisor to ensure your plan remains aligned with your evolving circumstances and long-term financial objectives.

