Are you ready to take control of your financial future and build a secure tomorrow? Smart financial planning is not just about saving money; it’s about creating a comprehensive strategy to achieve your financial goals. This article will guide you through actionable steps to build a robust financial plan, covering crucial areas like budgeting, investing, and debt management, ensuring a more secure and prosperous future. Discover how to effectively manage your finances and achieve financial freedom.
Setting Realistic Financial Goals

Setting realistic financial goals is crucial for successful financial planning. Avoid overly ambitious targets that can lead to disappointment and derail your progress. Instead, focus on achievable milestones that align with your current financial situation and long-term aspirations.
Start by assessing your current financial health. This includes understanding your income, expenses, assets, and debts. Use this information to create a realistic budget that accounts for both your needs and wants. Prioritize essential expenses and identify areas where you can cut back to free up funds for savings and investments.
Break down your long-term goals into smaller, manageable steps. For example, instead of aiming to save $100,000 in five years, set a monthly savings goal that contributes to that larger objective. This approach makes the process feel less overwhelming and keeps you motivated.
Regularly review and adjust your goals as your circumstances change. Life throws curveballs, and your financial plan should be flexible enough to adapt to unexpected events. This proactive approach ensures your goals remain relevant and achievable over time.
Consider seeking professional advice from a financial advisor. They can help you develop a personalized financial plan that aligns with your specific needs and risk tolerance, ensuring your goals are both realistic and effective.
Creating a Budget and Sticking to It

Creating a budget is fundamental to smart financial planning. It involves tracking your income and expenses to understand your spending habits and identify areas for potential savings.
Start by listing all sources of income, including salary, investments, and other earnings. Then, meticulously record all your expenses, categorizing them into necessities (housing, food, transportation) and non-essentials (entertainment, dining out).
Several budgeting methods exist, including the 50/30/20 rule (50% needs, 30% wants, 20% savings and debt repayment) or the zero-based budget (allocating every dollar to a specific category). Choose a method that aligns with your preferences and financial goals.
Sticking to your budget requires discipline and consistent monitoring. Regularly review your spending against your plan. Utilize budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track progress and make adjustments as needed. Identify areas where you can cut back on spending without significantly impacting your lifestyle.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting your budget is crucial. Life circumstances change, and your budget should reflect these changes. This proactive approach ensures your financial plan remains effective and helps you achieve your long-term financial goals.
Building an Emergency Fund
A crucial element of smart financial planning is establishing a robust emergency fund. This fund acts as a safety net, providing financial stability during unexpected events such as job loss, medical emergencies, or home repairs.
The recommended size of your emergency fund is typically 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses. This amount ensures you can cover essential costs like rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation even without a regular income stream.
Begin by setting a realistic savings goal. Start small if necessary; even saving a small amount consistently is better than not saving at all. Automate your savings by setting up regular transfers from your checking account to your savings account.
Consider using a high-yield savings account to maximize your interest earnings. While the primary goal is security, earning a bit of interest can help your fund grow faster.
Regularly review and adjust your emergency fund. As your income and expenses change, so should your savings goal. Aim to replenish the fund after any withdrawals to maintain its protective capacity.
Understanding Tax Planning
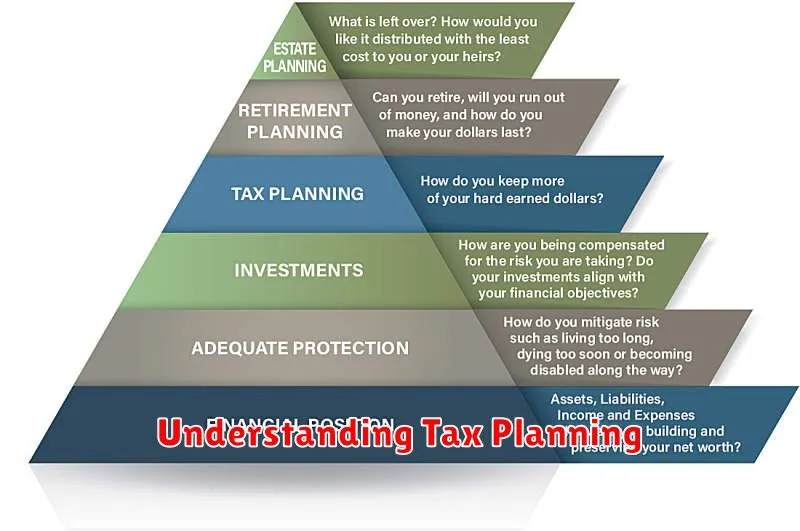
Tax planning is a crucial element of smart financial planning. It involves strategically managing your financial affairs to minimize your tax liability while remaining compliant with the law. Effective tax planning isn’t about avoiding taxes altogether, but rather about legally reducing your tax burden.
Key strategies include maximizing deductions, claiming eligible credits, and making informed investment decisions. Understanding different tax brackets and the implications of various financial choices is essential. For example, contributions to tax-advantaged retirement accounts can significantly reduce your taxable income in the present.
Professional advice is often beneficial, particularly for complex financial situations. A qualified tax advisor can help you develop a personalized tax plan tailored to your specific circumstances, ensuring you leverage all available tax advantages.
Proactive planning is key. Don’t wait until tax season to consider your tax implications. Integrate tax considerations into your financial decisions throughout the year to optimize your overall financial well-being.
Retirement Planning Strategies
Retirement planning requires a proactive approach, beginning well in advance of your intended retirement date. A key element is saving consistently, ideally contributing to a retirement account like a 401(k) or IRA, maximizing employer matching contributions where available.
Diversification of your investment portfolio is crucial to mitigate risk. Consider a mix of stocks, bonds, and potentially real estate, adjusting the allocation based on your risk tolerance and time horizon. Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation.
Estimating retirement expenses is essential to determine your savings goals. Consider healthcare costs, housing, travel, and other anticipated expenses. Using online retirement calculators can help you project your future needs and assess the adequacy of your savings.
Planning for healthcare costs is a critical aspect of retirement planning. Medicare doesn’t cover all expenses, so explore supplemental insurance options or consider a health savings account (HSA) to mitigate potential healthcare burdens in retirement.
Consider working longer, even part-time, to supplement your retirement income. This can delay the depletion of your savings and provide additional financial security. Explore options for phased retirement or consulting work in your field.
Seeking professional advice from a financial advisor can offer personalized guidance. A financial advisor can help you create a comprehensive retirement plan tailored to your specific circumstances, risk tolerance, and financial goals.
How to Manage Financial Risks
Effective financial risk management is crucial for securing your future. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to your financial well-being. Diversification is key; spreading your investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) reduces the impact of any single investment performing poorly.
Emergency funds are essential. Aim for 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in a readily accessible account to cover unexpected events like job loss or medical emergencies. This prevents you from taking on high-interest debt to cover unexpected costs.
Insurance plays a vital role in risk mitigation. Adequate health, life, disability, and property insurance protects against significant financial losses from unforeseen circumstances. Review your coverage regularly to ensure it aligns with your current needs and risk profile.
Debt management is paramount. High levels of debt increase vulnerability to financial shocks. Prioritize paying down high-interest debt and develop a budget to control spending and avoid accumulating unnecessary debt.
Financial planning with a professional can provide personalized guidance. A financial advisor can help you create a comprehensive plan to manage risk based on your individual circumstances, goals, and risk tolerance. Regularly review and adjust your plan as your life circumstances change.
Smart Saving Techniques

Smart saving is crucial for securing a strong financial future. It involves more than just putting money aside; it requires a strategic approach.
Budgeting is the cornerstone. Track your income and expenses meticulously to identify areas for improvement. Utilizing budgeting apps or spreadsheets can significantly aid this process.
Automate your savings. Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to a savings account each month. This ensures consistent contributions without requiring constant effort.
Prioritize high-yield savings accounts. These accounts offer better interest rates than traditional savings accounts, allowing your money to grow faster.
Explore different savings vehicles. Consider options beyond savings accounts, such as certificates of deposit (CDs) for longer-term goals, or retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs, leveraging tax advantages.
Set realistic financial goals. Having clear, measurable goals—like a down payment on a house or early retirement—provides motivation and direction for your savings strategy.
Review and adjust your plan regularly. Your financial situation will evolve, so it’s important to periodically assess your budget, savings goals, and investment strategies to ensure they remain aligned with your needs.
Avoid impulsive spending. By consciously curbing unnecessary purchases, you can significantly increase your savings.
Increase your income streams. Explore opportunities for additional income through side hustles or freelance work to accelerate your savings.
Using Technology for Financial Planning
Technology offers powerful tools for streamlining and enhancing financial planning. Budgeting apps like Mint or Personal Capital automatically categorize transactions, track spending, and provide insightful visualizations of your financial health. These tools help you identify areas for improvement and make informed spending decisions.
Investment platforms such as Fidelity or Schwab provide easy access to diverse investment options, allowing you to build a diversified portfolio aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Many platforms offer automated investing (robo-advisors) for simplified portfolio management.
Financial planning software can assist with long-term financial projections, retirement planning, and tax optimization. These programs often include features for simulating different scenarios, helping you make informed decisions about saving, investing, and debt management.
Secure online banking provides convenient access to your accounts, enabling you to monitor balances, transfer funds, and pay bills efficiently. The use of strong passwords and multi-factor authentication is crucial for maintaining the security of your online financial data.
Leveraging these technological advancements can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your financial planning process, ultimately contributing to a more secure financial future. Remember to choose reputable and secure platforms to protect your sensitive information.

